Why in news?
- India’s population growth has been a hot topic for decades, with projections placing it as the world’s most populous nation by 2023.
- However, a crucial, yet lesser-discussed aspect is emerging: declining fertility rates.
- This shift in population dynamics, known as India’s demographic transition, presents both challenges and opportunities for India’s future.
- While a larger population can translate to a larger workforce, a decline in fertility rates can usher in a period where the working-age population outnumbers dependents, creating a potential economic boom if the right conditions are met.
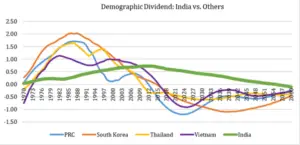
Understanding Demographic Transition and Dividend
- A demographic transition signifies a change in a population’s composition over time.
- This shift is driven by factors like birth and death rates, migration patterns, and socioeconomic conditions.
- One key outcome of this transition is the demographic dividend – a phenomenon where the working-age population (adults) outnumbers dependents (children and elderly).
- This larger working-age population has the potential to fuel economic growth and development, provided the right conditions are in place.
Factors Behind India’s Demographic Transition
- Several factors are propelling India’s demographic transition:
- Rapid Economic Development:
- India’s economic boom, particularly since the early 2000s, has significantly impacted its demographics.
- Improved living standards, better healthcare, and increased access to education contribute to lower birth rates.
- Reduced Infant and Child Mortality:
- As healthcare improves and child mortality declines, families feel secure having fewer children, leading to a decline in total fertility rate (TFR).
- Rise in Women’s Education and Work Participation:
- Increased education and workforce participation of women play a vital role.
- Empowered women tend to have fewer children and delay childbirth, further reducing TFR.
- Improvement in Housing Conditions:
- Better housing and access to basic amenities lead to a better quality of life, influencing family planning decisions.
- Smaller families may be preferred with improved living conditions.
Challenges of Demographic Transition
- While initially beneficial, India’s demographic transition also presents challenges:
- Shifting Dependency Ratio:
- While a decline in TFR initially reduces dependency ratio, it eventually leads to a larger elderly population. This strains healthcare and social welfare resources, similar to situations in developed countries.
- Uneven Transition Across States:
- The decline in fertility rates varies across states. Some larger states, like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, may take longer to reach replacement level fertility, exacerbating regional disparities in development.
- Labour Productivity and Economic Growth:
- While the demographic transition can boost labour productivity and economic growth, challenges remain.
- These include managing an aging workforce and ensuring adequate skills development for the younger generation.
- Shifting Dependency Ratio:
Opportunities from Demographic Transition
- Despite the challenges, India’s demographic transition presents significant opportunities:
- Enhanced Labour Productivity:
- A decelerating population growth can lead to a higher per capita availability of capital resources and infrastructure, ultimately boosting labour productivity.
- Reallocation of Resources:
- Decreasing fertility rates allow for reallocating resources towards education and skill development, improving human capital and workforce productivity.
- A declining TFR can lead to fewer children in schools, requiring potentially less spending on education.
- Increased Women Participation in Workforce:
- Childcare responsibilities are a major factor hindering women’s workforce participation. With less time spent on childcare, a rise in women joining the workforce is expected.
- This is already evident in states like Kerala with higher female participation in programs like MGNREGA.
- Spatial Redistribution of Labour:
- Movement of labour from surplus regions to growing industrial areas can create a balanced labour market.
- This can be facilitated by modern sectors in southern states attracting labour from the north.
- However, this needs to be accompanied by improved working conditions, elimination of wage discrimination, and institutional safeguards for migrant workers.
- Enhanced Labour Productivity:
The Road Ahead
- As highlighted in the Asia 2050 report, India can become a major economic player by capitalizing on these opportunities.
- This requires focusing on sectoral and spatial workforce redistribution, skill development, and increasing women’s participation in the workforce.
- Effectively harnessing the demographic dividend can significantly contribute to India’s global economic competitiveness.
- India’s evolving population dynamics necessitate careful policy formulation, particularly in healthcare, education, and skill development.
- Policies addressing the specific needs of women and marginalized groups are crucial to ensure inclusive growth and development in this era of demographic transition.
People also ask
Q1: What is demographic transition?
Ans: Demographic transition refers to a long-term shift in a population’s composition. This change is driven by factors like birth and death rates, migration patterns, and socioeconomic conditions. It typically involves a decline in birth rates and a rise in life expectancy, leading to a larger working-age population compared to dependents (children and elderly).
Q2: What is the demographic dividend?
Ans: The demographic dividend is a potential economic benefit that arises from a large working-age population. With more people working and fewer dependents, a country can experience faster economic growth and development.
Q3: How will India’s demographic transition impact its future?
Ans: India’s demographic transition presents both challenges and opportunities. By effectively managing these dynamics and implementing the right policies, India can leverage its demographic dividend to achieve significant economic growth and become a major player in the global economy.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for your comments you can share with your friends and family member.you can subscribe my newsletter.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.