Why in news?
- India’s soil erosion crisis has reached alarming levels, posing significant threats to agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
- A recent study utilizing the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) has unveiled the gravity of the situation, highlighting key hotspots and factors contributing to soil erosion.
Understanding Soil Erosion:
- Soil erosion is a natural process involving the movement or displacement of soil particles from one location to another.
- This movement occurs through various mechanisms, primarily driven by natural forces like wind, water, and glaciers, as well as human-induced activities.
- Factors Contributing to Soil Erosion:
- Natural Causes:
- Wind Erosion: In areas with sparse vegetation cover, strong winds can pick up loose soil particles and transport them over long distances, causing erosion.
- Water Erosion: Heavy rainfall, surface runoff, and flowing water in streams and rivers can detach and transport soil particles, particularly on sloped land without adequate vegetation cover.
- Glacial Erosion: Glaciers and ice movement can scrape and transport large volumes of soil and rock debris, contributing to erosion in mountainous regions.
- Human-Induced Factors:
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture, urbanization, or logging removes the protective vegetation cover that holds soil in place, making it susceptible to erosion.
- Poor Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming methods such as excessive tilling, monoculture cropping, and improper land management contribute to soil degradation and erosion.
- Overgrazing: Uncontrolled grazing by livestock can lead to the destruction of vegetation cover, exposing soil to erosion by wind and water.
- Construction Activities: Land clearing, excavation, and improper construction practices disrupt soil stability, leading to erosion, especially in vulnerable areas.
- Natural Causes:
Status of Soil Erosion in India:
- Key Findings from the Study:
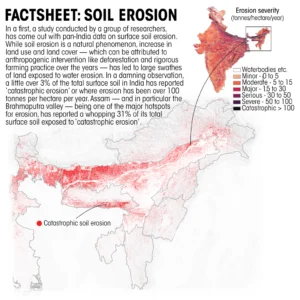
- The study reveals that approximately 30% of India’s landmass is experiencing “minor” soil erosion, while 3% is facing “catastrophic” topsoil loss.
- This indicates a significant challenge to soil conservation efforts in the country.
- Hotspots Identified: The Brahmaputra Valley in Assam and Odisha are identified as critical hotspots for severe erosion, highlighting the urgent need for targeted conservation measures in these regions.
- Catastrophic Erosion Defined: Catastrophic erosion refers to the loss of over 100 tonnes of soil per hectare annually, indicating a severe and rapid depletion of topsoil, which is essential for supporting agricultural productivity and ecosystem stability.
- Challenges Related to Soil Health in India:
- Low Organic Carbon Content: The decline in soil organic carbon (SOC) content is a major concern, as organic carbon is crucial for maintaining soil fertility, structure, and water retention capacity.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Many Indian soils suffer from deficiencies in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth and productivity.
- Water Management Issues: Water scarcity and improper irrigation practices exacerbate soil degradation, leading to salinization, waterlogging, and reduced soil fertility.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Land fragmentation, population pressures, and economic constraints hinder the adoption of sustainable soil management practices, posing challenges to soil conservation efforts in India.
Conclusion:
- India’s soil erosion crisis demands urgent attention and concerted efforts from various stakeholders including government, farmers, and researchers.
- By implementing effective soil conservation strategies and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, we can mitigate soil erosion, preserve soil health, and ensure long-term agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
People also ask
Q1: What is soil erosion, and why is it a concern in India?
Ans: Soil erosion refers to the process of soil particles being displaced or washed away from their original location. It is a concern in India due to its adverse effects on agricultural productivity, environmental sustainability, and land degradation.
Q2: What are the main causes of soil erosion in India?
Ans: Soil erosion in India is primarily caused by natural factors such as wind, water, and glaciers, as well as human-induced activities including deforestation, poor agricultural practices, overgrazing, and construction activities.
Q3: How severe is soil erosion in India?
Ans: Studies indicate that around 30% of India’s landmass is experiencing varying degrees of soil erosion, with approximately 3% facing catastrophic topsoil loss. Certain regions like the Brahmaputra Valley in Assam and Odisha are identified as critical hotspots for severe erosion.
Q4: What are the consequences of soil erosion?
Ans: Soil erosion can lead to reduced agricultural productivity, loss of fertile topsoil, increased sedimentation in water bodies, degradation of ecosystems, and heightened vulnerability to natural disasters like floods and landslides.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/lv/register-person?ref=B4EPR6J0