Table of Contents
Why in news?
- The Great Nicobar project has of lately attracted a lot of attention mainly because of its planned location and environmental consequences.
- Since the Indian government aims at increasing the capacity and efficiency of infrastructures, meeting the ever-demanding aspiration of defense especially in the marine region, and promoting development in the region, maintaining ecological balance is of essence.
- In other blogs in this series, Explaining the Great Nicobar Project, another one is going to uncover the detailed strategic rationale for this project and the environmental implications of the project and the Great Nicobar as it fits into the fold of the National Monetisation Pipeline.
Strategic Imperative of the Great Nicobar Project
Enhancing Maritime Security
- Geographic Significance:
- Great Nicobar is thus the part of India’s territory located in the southernmost part and it occupies the extremely important place in the Indian Ocean.
- It is strategically situated very close to the Malacca Strait, one of the most important sea channels globally that is crucial for foreign commerce and with a constantly increasing quantity of traffic.
- Military and Strategic Presence :
- The development of the project shall boost India’s maritime domain awareness and defense immensely.
- To maintain control of the island and promote Indian strategic influence, it will be possible to build naval bases and other forms of military infrastructure necessary to control the movement of ships and maintain stability in a region which is known for numerous powers’ tensions and conflicts.
Boosting Economic Development
- Infrastructure Development :
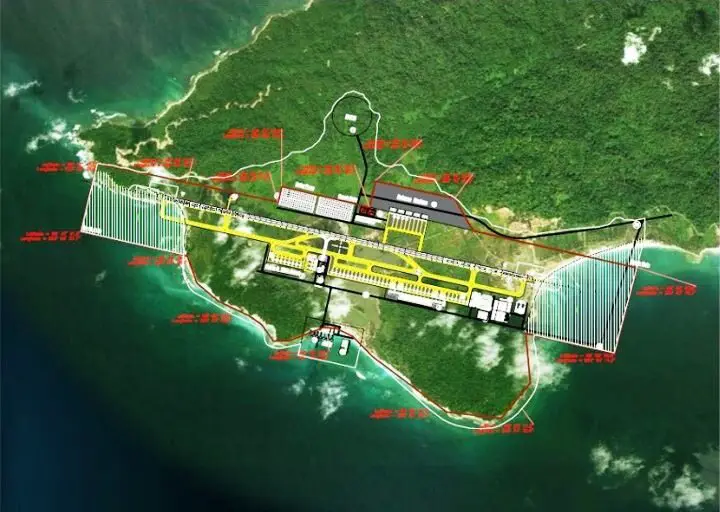
- The Great Nicobar has included in its broiler the establishment of a transhipment port, airport, a power plant and new township.
- Such advancements are about to shape economic growth thus facilitating employment slots and empowering regional growth.
- Enhancing Connectivity:
- Regarding the economic impact, enhancement of the connectivity between the island and the rest of India in terms of business, tourism and investment.
- This connectivity is paramount to his envisaged integration of the island’s economy into the regional, national and global economy systems.
Aligning with National Objectives
- Complementing National Initiatives :

- Narendra Modi’s PM Gati Shakti and the NMP represent the large-scale initiatives to which this project connects on the national level in India.
- Whereas the PM Gati Shakti is dedicated to enhancing the interlinkage of infrastructure facilities across the country, the NMP is customized to utilize the existing infrastructure assets in order to attract investments for new infrastructural initiatives hence making a positive cycle of development.
- Strategic Autonomy:
- By so doing, India could deny a foreign power further opportunity to deepen its props in the Great Nicobar region, and the development of this region will also afford the nation more strategic depth in the maritime domain to check external powers’ pressures while asserting increased independence in procurement of security as well as trade needs.
Environmental Concern
Ecological Sensitivity
- Biodiversity Hotspot Great Nicobar Island is actually situated in one of the seventeen world’s hotspots of biological diversity. The geographical features of the island consist of jungles; mangrove forests; sea grass beds; coral reefs; proposing a rich and diverse vegetation and animal species that are either distinct or threatened.
- Potential Habitat Destruction The activities that may arise as a result of construction in relation to this project may bring about destruction of habitats of the species in this island hence interfering with the ecological systems. Rising human activities such as deforestation, land reclamation, and other developments may threaten animals’ breeding grounds thus reducing the number of species.
Climate Change Impact
- Rising Sea Levels:
- like many other islands many low profile, Great Nicobar island is endangered by climate change which causes the sea levels to rise.
- This development would worsen the problem of coastal erosion hich is likely to become a major source of flooding.
- Carbon Emissions:
- Among the development activities was the construction of a power plant; it was noted that this came with negative impacts, such as climate change through the emission of carbon.
- There is, therefore, the need to address energy requirements sustainably in an effort to reduce each of these impacts.
Indigenous Communities
- Cultural Displacement :
- The aboriginal tribes of Shompens and Nicobars have dwelled in Great Nicobar for quite some time.
- The large scale developments may also interfere with their un-modified lifestyle and thereby bring into the society a new culture which may lead to loss of culture.
- Access to Resources :
- It might lock indigenous communities out from resources that they depend on for their subsistence within the project area.
- Health and other rights for women and children, for instance, need to be protected from exploitation, and this is why liberating them to have their rights recognized and fulfilled is fundamental to the development of such an economy.
National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP): Connection
- National Monetisation Pipeline is a latest buzzword in India but still it has not been defined in any specific and Legal terminology used in its definition is Pipelines, Products & Services.
- The NMP is an economic plan launched by the Indian government to convert the centrality of the assets in the form of leasing and other arrangements.
- It seeks to raise nearly Rs 6 lakh crore from_assets across roads, railways, power ,oil and gas pipelines and the like in a four year plan ( FY 2021-22 to FY 2024-25).
Objectives and Achievements
- Financial Goals :
- The narrow meaning of the NMP aims at just increasing funds for new infrastructural development through efficient use of the available assets.
- For three years, starting with annual interest, the actual amount of assets as of the first three years is Rs 3. Out of 1,85 lakh crore intended, 85 lakh crore have been monetized, which shows the good progress in achieving the target.
- Enhancing Infrastructure
- The funds are expected to be available for investment under the NIP, anchored at Rs 111 lakh crore in the six-year FY21- FY25 period from proceeds of NMP.
- This integration is targeting to improve infrastructural development all over the country.
Ties to the Great Nicobar Project
- Funding Mechanism
- The remaining part of the systematic review will give an idea about applying the NMP in the context of the Great Nicobar project , with an explicit possibility to use the funds, which can be received after the monetization of the assets.
- This approach supports the government’s goal set out in the NIMp of mobilising capital for the development of new infrastructure projects but making efficient use of the available resources.
- Strategic Alignment
- Since the element of the NMP that relates to improving infrastructure is consistent with the strategic objectives of the Great Nicobar project, the results are also consistent with expectations.
- Thus, it can be stated that both initiatives represent a desire to improve accessibility, economic growth, and strategic positioning as forms of a complex development strategy.
Conclusion
- It is the Great Nicobar project which entails a strong strategic plan of sorts for India that could apparently build upon a seemingly stronger naval security, the growth of economic zones and provide for a congruence of objectives.
- Yet it also creates great environmental and social problems.
- Achieving all these competing goals entails adopting a multi-perspective approach that would incorporate strategic priorities with environmental preservation as well as a population’s well-being.
- Thus, the Great Nicobar project can and should be considered from the perspective of modern India and its sustainable development, adopting the best international practices and applicable to Indian conditions, taking max thoroughness of environmental impacts assessment, cooperation with local communities.
FAQS
Q1: What is this Great Nicobar Project all about?
Ans: The Great Nicobar Project is a gigantic development plan for Great Nicobar Island that has the proposition of augmenting strategic facilities. They consist of the building of a transshipment port, international airport, a power plant, and township development areas meant to improve regional economic yields and sea security.
Q2: What makes Great Nicobar Island important ?
Ans: Great Nicobar Island is of significant geopolitical importance due to its location close to the Malacca Strait which is one of the most important sea lanes of communications in the world that provides passage to nearly forty percent of the world’s trading shipping. That is why the development of the infrastructure of the island will work to sustain and improve India’s ability to monitor and control the seas and help consolidate the country’s position in the Indian Ocean.
Q3: In what way will the project increase maritime security?
Ans: Thus, the construction of naval bases and similar facilities on Great Nicobar will strengthen India’s control over sea routes and protect the Indian Ocean from potential threats. This increased visibility shall assist in shoring up national security objectives as well as facilitating stability within the region.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.