Table of Contents
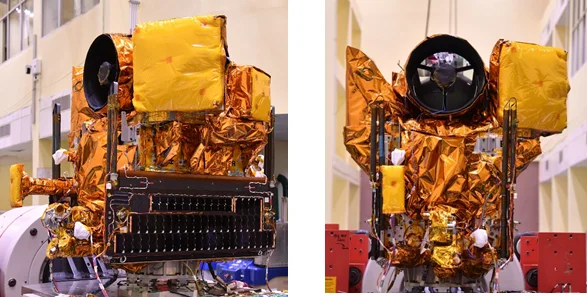
Photo Credit: ISRO
Why in news?
ISRO is one of the pioneer organizations when it comes to technology, as especially when it comes to space technology and satellite technology. One of the latest Earth Observation Satellite, EOS-08 mission is the perfect example of how ISRO is leaving no stone unturned. Standing to be launched by the SSLV-D3, EOS-08 is not just another satellite in the orbit, but much more than that. It is a qualitative learning from previous satellite mainframe systems, earth observation and assimilation of new technologies with an aim of improving on the future of space travel possibilities.
Overview of the EOS-08 Mission
Hence, the major aims of the EOS-08 mission are as follows: design and development of a microsatellite which will be effective when launched; developing payload instruments that are compatible with the goals of a microsatellite bus; integration of new technologies that are integral to future operational satellites. Built on the Microsat/IMS-1 bus, the EOS-08 satellite carries three payloads: EOIR Electronic Payload, GNSS-R Electronic Payload, Electronic SiC UV Payload, and SiC UV Payload. These payloads are as follows, all of which work together to support the mission objectives:
Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR)
The EOIR payload is an extension of the EOS-08 satellite that has capabilities to support imaging in the Mid-Wave IR (MIR) and the Long-Wave IR (LWIR). This capability enables the sat to work during the day and night which makes it a useful tool in so many differ applications. Some of these are satellite based observation, disaster observation, environment observation, fire observation, volcanic activity observation and industrial and power plant disasters observation. The option in the EOIR payload to work under different light is that data important for various Earth phenomena can be collected without interruption during a 24-hour period.
Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry Payload (GNSS-R)
The GNSS-R payload is actually a revolutionary concept in the field of remote sensing and this effort can set an example and show how GNSS-R based remote sensing can be used in different fields. They are ocean surface wind analysis, quantitative assessment of soil moisture, cryospheric studies especially in Himalayan zone, flood identification, and identification of water bodies in land mass. This payload employs the reflected GNSS signals as a way of observing the earth which is a unique method of imaging the earth that supplements the satellite imaging. One should also note that high accuracy of the monitored and analyzed environmental parameters creates opportunities to study and deal with numerous phenomena in agriculture, disaster response, and climate sciences.
SiC UV Dosimeter
Another state-of-art payload on-board EOS-08 is SiC UV Dosimeter which was developed to measure the UV irradiance at the viewport of the Crew Module in the planned Gaganyaan Mission. It also functions as a high dose alarm for gamma radiation; its place in the safety of future manned spaceflight cannot be overemphasized. Owing to the effective quantitative assessment of UV exposure and gamma radiation, the SiC UV Dosimeter plays a role in the larger interest of space research and the protection of human life as ISRO plans for manned space missions. Satellite Configuration and Specifications
Satellite Configuration and Specifications
As to the launcher, EOS-08 is designed for operation in Circular Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at altitudes of 475km and inclination of 37deg. 4°. The satellite has a mission duration of 1 year to accomplish the GEO/EOS and data collection responsibilities planned for the vehicle. It has a mass of about 175. 5 kg, EOS-08 is very portable but it has a high power output of roughly 420 W to power most of its features. The satellite has an interface with the SSLV-D3/IBL-358 launch vehicle facilitating compatibility with the launch vehicle system.
Advancements in Satellite Mainframe Systems
EOS-08 is a new generation of satellite mainframes, following the previous generations of EOS-05 and EOS-06; it also has a new Avionics system called Communication, Baseband, Storage and Positioning (CBSP) Package. This integrated system offers a number of functions in one single unit, which simplifies the complexity and improves the whole functional performance of the satellite. The CBSP package is built with cold redundant systems, COTS components and evaluation boards and it has data storage capability of up to 400 Gb. Besides, this approach also contributes on the reliability of the system and showed that affordable electronic components can be implemented on space missions.
Besides the CBSP package, EOS-08 comes with a structural panel possessing a PCB, an embedded battery, Micro-DGA, M-PAA, and a flexible solar panel. Each of them serves purpose when it comes to efficient working and maneuver of the satellite. For example, the flexible solar panel uses a foldable substrate of the solar panel, glass fiber reinforced plastic tube, carbon fiber reinforced plastic honey comb rigid end cap and provides increased power output and structural enhancement. A pyrolytic graphite sheet diffuser plate is employed similar to the one used in the Herschel mission due to its high thermal conductivity of 350 W/mK, while at the same time lowering the satellite mass and affecting the thermal design of the satellite.
Innovations in Antenna and Communication Systems
In line with this, when it comes to the design of Antenna Pointing Mechanisms, EOS-08 has a miniature dimension. With a rotational speed of 6 degrees per second and position accuracy of ±1 degree, this system improves on the communications of the satellite by being able to orient the satellite in a correct position with ground stations and other satellites. The miniaturized phased array antenna takes things a notch higher in terms of communication effectiveness and reliability due to faster data transfer rates.
The satellite also introducing a new concept in X-band data transmission; pulse shaping and Frequency Compensated Modulation (FCM) for X-Band data transmitter. They explain that this innovation provides an improved functionality of the transmission, of large volumes of data especially necessary for earth observation missions. Further, its battery management system uses SSTCR-based charging & bus regulation including or excluding strings at a 6 Hz rate for maximum power efficiency and operation continuity.
Enhancements in Thermal Management and Structural Design
Thermal control is one of the key concerns of any satellite mission and EOS-08 has used many modern and innovative methodologies and materials for controlling the temperatures of the components of the satellite. These are AFE BGA, Kintex FPGA, Germanium Black Kapton, and STAMET (Si-Al Alloy) Black Kapton components and all help the satellite to function in the extreme environment of space. The mission also has reaction wheel isolators for damping the vibrations that might affect the inertial system of the satellite.
Technologically speaking, EOS-08 added a novel concept to the structural design of housekeeping panel integration: the hinge-based fixture. This innovation dramatically cuts the time required in Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) phase, thus enhancing the speed of preparing and moving missions. There is also an auto-launch pad initialization integrated in the satellite to minimize on the chances of an error in the process of launch.
Conclusion
The EOS-08 mission is one of the best examples of the fact that ISRO is exploring fresh opportunities in satellite engineering and Earth observation. With the high advance payloads, improved mainframe system and communication system, the EOS-08 can greatly contribute to different field such as disaster management, environmental monitoring and space exploration. When ISRO is building and launching advanced series of satellites in terms of EOS-08, the country is making its own stand through space science and technology.
FAQS
Q1: What is the EOS-08 mission?
Ans: The EOS-08 mission is an Earth Observation Satellite launched by ISRO, designed to enhance satellite technology and provide valuable data for applications such as environmental monitoring, disaster management, and more.
Q2: What are the primary objectives of EOS-08?
Ans: The primary objectives include designing a microsatellite, developing payload instruments, and incorporating new technologies for future operational satellites.
Q3: What payloads does EOS-08 carry?
Ans: EOS-08 carries three payloads: the Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR), Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry payload (GNSS-R), and SiC UV Dosimeter.
Q4: What are the applications of the EOIR payload?
Ans: The EOIR payload is used for satellite-based surveillance, disaster monitoring, environmental monitoring, fire detection, and more.
Real Estate There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
BaddieHub Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.