Context
- As part of the larger Kaleshwaram project, investigation teams for the project are presently evaluating the state of the coffer dam’s removal at the Medigadda Barrage.
- Investigative teams are working with the National Remote Sensing Agency to determine this.
- The investigation’s main focus is gathering and examining satellite images of the targeted area.
- The provision of precise and comprehensive information is greatly aided by the National Remote Sensing Agency’s proficiency with satellite imagery.
- The goal of using cutting-edge technology is to ascertain the coffer dam’s present condition and how it affects the Kaleshwaram project.
About The kaleshwaram Lift irigation Project
Kaleshwaram Project Location:
-
-
- The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is situated on the Godavari River in Kaleshwaram, Bhupalpally, Telangana, India.
-
- World’s Largest Multi-Stage Lift Irrigation Project:
-
- Currently, KLIP holds the distinction of being the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.
-
- Farthest Upstream Influence:
-
- The project’s influence extends upstream to the confluence of the Pranahita and Godavari rivers.
-
- Pranahita River Confluence:
-
- The Pranahita River, formed by the convergence of smaller tributaries including the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers, contributes to KLIP’s far-reaching impact.
-
- Seventh-Largest Drainage Basin:
-
- KLIP operates within the seventh-largest drainage basin on the subcontinent, characterized by an estimated annual discharge exceeding 6,427,900 acre-feet (7,930 cubic hectometres) or 280 TMC.
-
- Untapped Resources:
-
-
-
- The Pranahita River’s potential remains largely untapped due to its course through dense forests and ecologically sensitive zones, including wildlife sanctuaries.
-
-
-
- World’s Largest Multi-Stage and Multi-Purpose Lift Irrigation Project:
-
- KLIP boasts the title of being the largest multi-stage and multi-purpose lift irrigation project globally.
-
- Previous Name:
-
- Formerly recognized as the Pranahita-Chevella Lift Irrigation Project.
-
- Key Feature:
-
- A notable aspect of KLIP is its array of underground and surface water pumping stations, acclaimed as the world’s largest such structures.
-
- Extensive Stretch:
-
- Spanning over 300 km, the lift irrigation system efficiently elevates significant water volumes from rivers or reservoirs.
- This water is then distributed through channels or stored in additional reservoirs before being pumped to subsequent stations.
-
- Water Supply Objective:
-
- The project’s primary goal is to provide water to 45 lakh acres in Telangana.
-
- Commencement and Utilization:
-
- Initiated in 2016, KLIP is set to utilize approximately 283 TMC of water sourced from the Godavari River.
- Its purpose is to facilitate irrigation and supply drinking water to 13 districts within Telangana.
- Efficient Water Distribution Infrastructure:
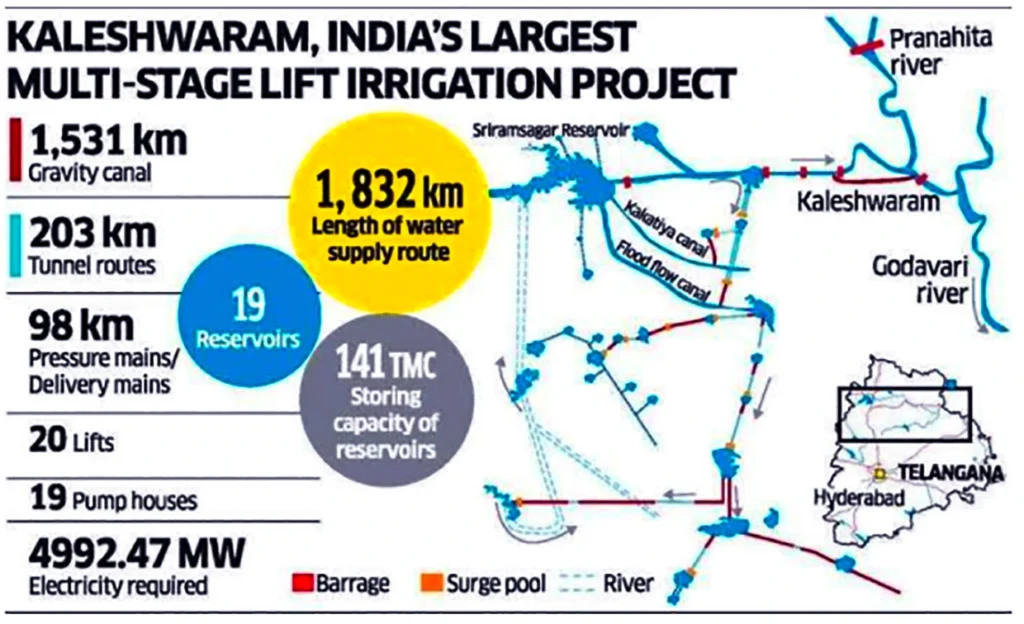
- Landmark 203 km Gravity Tunnel:
- A monumental feat in engineering, the project includes a remarkable 203 km gravity tunnel, further enhancing the efficiency of water transport.
- Delivery and Pressure Mains:
- The system also incorporates 98 km of delivery and pressure mains, contributing to the seamless and effective flow of water throughout the network.
3. Gravity Canal Network:
- Encompassing an extensive 1,531 kilometers, the gravity canal system serves as a pivotal component for water distribution
- Landmark 203 km Gravity Tunnel:
-
About the Dam Safety Act
- December 2021 saw the implementation of the Dam Safety Act, 2021.
- The act intends to solve the long-standing need to address concerns about the security of significant dams across the nation.
- The Act covers those dams having a height of over 15 meters and between 10 and 15 meters with specific restrictions.
- It also provides for the surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance of certain dams for the prevention of disasters related to dam failure, aside from institutional mechanisms to ensure their safe functioning.
Navigating Success: Unravling the wonders of the kaleshwaram Project
- Establish two national organizations:
- The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) works to carry out policies and resolve outstanding disputes between the two States, while the National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS) aims to develop dam safety policies and suggest relevant legislation.
- The governing body will be the NDSA.
- Create two State Level Institutions:
- Dam owners shall be accountable for the design, building, upkeep, and management of dams. The law also calls for the establishment of State Committees on Dam Safety and State Dam Safety Organizations.
For More Information click here

Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for your comments you can share with your friends and family member.you can subscribe my newsletter.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.